Application of CNF to IoT devices in harmony with natural cycles
April 7, 2022
Short summary:
The inventors have successfully developed an IoT device made of cellulose nanofibers that can be “returned to the ground”.
The device is made solely from the bounty of nature, including paper (cellulose nanofibers), metal, and stone (minerals). As a result, when the product is left in the natural environment after use, it can be “returned to the ground” in approximately one month.
Description:
The existence of IoT devices that are used to collect weather, traffic volume, and health information in a variety of fields, including agriculture, medicine, urban management, and manufacturing and can be connected to various locations is becoming indispensable. There is no doubt that the number of IoT devices will continue to grow. However, it is necessary to consider the collection of devices that have reached the end of their useful service life and environmental pollution caused by electronic waste.
Generally, as the functions, including information collection (monitoring) and wireless information transmission of electronic devices increase, so too does the effort and cost required to dispose of them.
Nano-paper is clear, and like glass does not expand and contract when heat is applied. It also has characteristics that make it suitable for use as an electronic device substrate, such as a smooth surface, as well as the lightness, flexibility, and biodegradability of paper. Harnessing these excellent characteristics, we have developed a variety of paper electronic components, such as paper memory and paper transistors, using nano-paper as a substrate. However, in order to make electronic circuits and devices from paper, it is necessary to assemble a range of paper electronic components and create a circuit without compromising the biodegradability of paper.
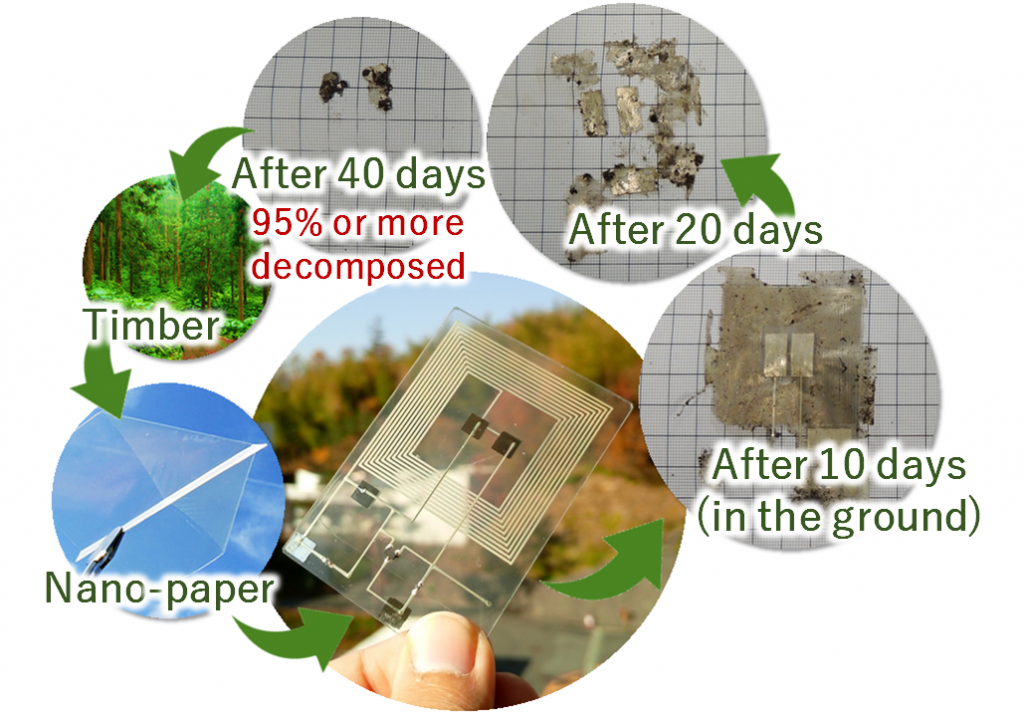
In this study, a research group at Osaka University evaluated nano-paper as a dielectric layer of a capacitor, one variety of passive element (*1). Capacitors are essential elements in circuits used to process sensor information and transmit it wirelessly. As a result, it has been revealed that it has more than three times the performance of conventional polymer materials, such as PET and polyimide, and has excellent lamination properties. In addition, nano-paper capacitors using nano-paper as a dielectric layer have been found to be applicable to humidity sensors, whose performance changes with humidity levels. Therefore, when a coil, resistor or nano-paper capacitor were mounted on a nano-paper substrate using only a printing and coating process, we succeeded in creating a nano-paper IoT device in which the radio signal changes according to changes in humidity. Nano-paper IoT devices do not use plastic substrates or adhesives that prevent them from decomposing, and because they are mostly made of “paper”, more than 95% of the total volume decomposed in the ground after 40 days. Paper-based nano-paper IoT devices are expected to offer a new concept for the realization of environmentally friendly IoT devices that can be easily installed anywhere.
These results demonstrate the performance of a paper-based, biodegradable IoT device prototype. If we are able to realize IoT devices with higher performance in the future that can be “returned to the ground”, they can be used anywhere, just like the plants and flowers that color our lives, enabling environmental monitoring that is in harmony with natural cycles. They could be installed on road signs to collect detailed weather information at each intersection, or installed at the entrance of each home to provide real-time and detailed information on disasters around the home.
Benefits:
Land
Benefits Description:
The results of this research demonstrate a new concept for biodegradable IoT devices that are in harmony with natural cycles through “decomposition by design” and can be installed in locations and in numbers that are difficult to recover. Paper is an essential element in achieving this concept. We hope this can serve as an example of an electronic device that takes advantage of the properties of paper, and accelerate research into the field of “paper electronics” that is sustainable and has low environmental impact.
Technology type:
Process, Material, Device or equipment
Developed in:
Japan
Technology appraisal:
Mr. Hiromichi Akimoto, Albatross Technology Co., Ltd., a joint research partner, was awarded Tech Rocketship Award 2019/2020 of the Clean Growth-Approaching Decarbonization category.(https://www.events.great.gov.uk/ehome/ukinjapan/tech-rocketship-awards-2019-20/winners-en)
DEVELOPMENT STATUS:
Readiness level (TRL)
Proof of concept (TRL 3-4)
CONDITIONS FOR USE:
Collaboration type
R & D contract or research collaboration
State of Development / Opportunity / Seeking:
・Available for exclusive and non-exclusive licensing
・Exclusive/non-exclusive evaluation for defined period (set up for options)
・Collaborative/supportive research
※Seeking
1. Development partner
2. Licensing
WIPO GREEN Database Website:
https://wipogreen.wipo.int/wipogreen-database/database
Figures:
Contact:
![]()